
- Function of free nerve endings in skin skin#
- Function of free nerve endings in skin code#
- Function of free nerve endings in skin free#
These are the most common type of nerve ending and are abundant in the skin. The dermis contains hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous (oil) glands, blood vessels, nerve endings, and a variety of touch receptors. They have no capsulated ends and Complex sensory structures. These are mainly afferent nerve fibers that send signals to a sensory neuron and function as cutaneous nociceptors invertebrates to detect stimuli, often resulting in pain.
Function of free nerve endings in skin free#
Note: Free nerve endings or FNE are also known as bare nerve endings.
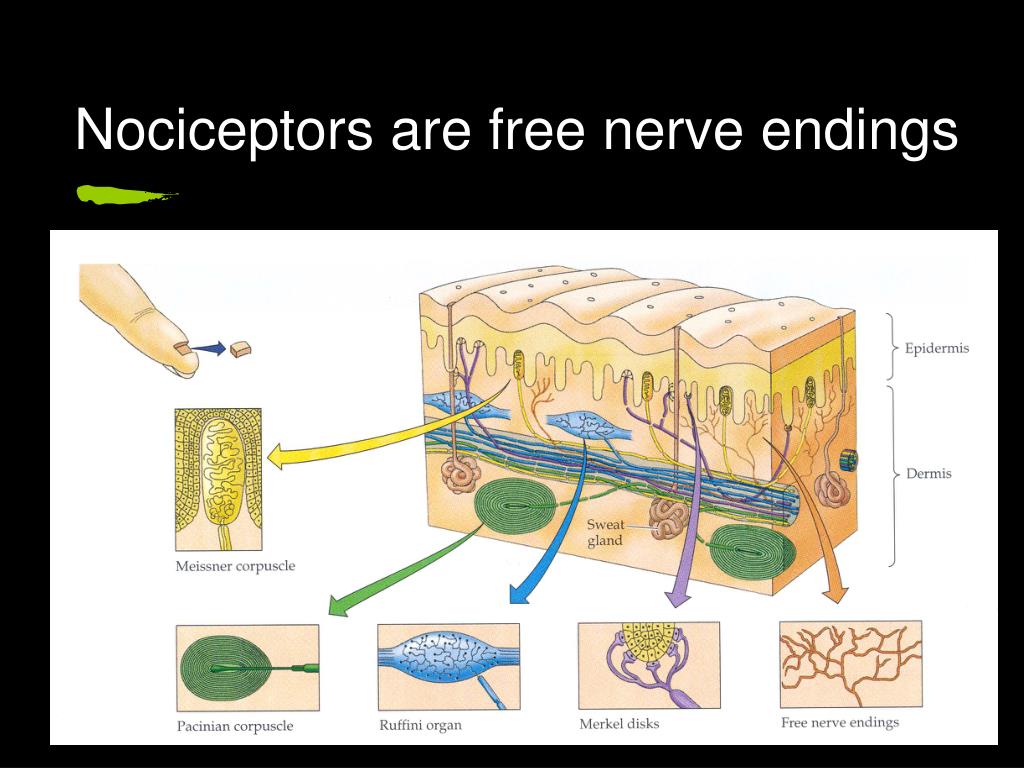
They are slow to adjust to a stimulus and so are less sensitive to abrupt changes in stimulation. Free nerve endings are sensitive to painful stimuli, to hot and cold, and to light touch. Group A and group C nerve fibers are two of the three classes of nerve fibers classified by Erlanger and Gasser. Free nerve endings are the most common nerve endings in skin, and they extend into the middle of the epidermis. Nociceptors are sensory neurons that respond to damaging stimuli. Mechanoreceptors are sensory cells that react towards mechanical pressure. Free nerve endings-are the most common type of nerve endings, they are of various types and respond to various stimuli, but are most commonly associated with temperature and pain.
Function of free nerve endings in skin code#
Thermoreceptors are non specialized sense receptors that code changes in temperature.
Function of free nerve endings in skin skin#
Slowly adapting mechanoreceptors are Merkel and Ruffini corpuscle end-organs and also some FNE. What do nerve endings in the skin detect Free nerve endings can detect temperature, mechanical stimuli (touch, pressure, stretch) or danger (nociception). Intermediate adapting are some free nerve endings. Rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors are Meissner corpuscles end-organs, Panichian corpuscles end-organs, hair follicle receptors, and a few free nerve endings. They have different fiber types such as A-delta fibers and C fibers and different rates of adaptations that are rapidly adapting, intermediate adapting, or slowly adapting.īelow are the different types of adaptations, stimulus modalities, and fiber types. In other words, they express polymodality. Thus, different free nerve endings work as thermoreceptors, cutaneous mechanoreceptors and nociceptors.
Therefore, they work as thermoreceptors, cutaneous mechanoreceptors, and nociceptors and therefore are polymodality. Free nerve endings can detect temperature, mechanical stimuli (touch, pressure, stretch) or danger (nociception). The free nerve ending is unencapsulated nerve endings that are found in the skin and stimulate sensations like touch, pressure, stretch, or even danger. They have different rates of stimulus modalities as well as different rates of adaptations and fiber types. Other articles where free nerve ending is discussed: senses: Mechanical senses: The first three, free nerve endings, hair follicle receptors, and Meissner. Intraepidermal free nerve endings are entirely enwrapped within the gutters of keratinocyte cytoplasm and form en passant synaptic-like contacts with.

Hint: Free nerve endings are unencapsulated nerve fiber mainly found in the skin and have no complex sensory structures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
